Apa yang dimaksud dengan NURBS?
April 6th 2006 6 April 2006
This article explains the term NURBS, describes basic properties of NURBS curves and surfaces, and gives examples how they are used in 3D modeling. Artikel ini menjelaskan istilah NURBS, menjelaskan dasar properti NURBS Curves dan permukaan, dan memberikan contoh bagaimana mereka digunakan dalam 3D modeling.
To understand this article you should have basic knowledge about vector and 3D graphics. Untuk memahami artikel ini, Anda harus mempunyai pengetahuan dasar tentang vector dan grafis 3D.
Curves in computer graphics Curves di komputer grafis
Curves are found in various areas of computer graphics. Curves terdapat di berbagai bidang komputer grafis. They are used when creating 3D models, vector images, animations, or for example in definition of TrueType fonts. There is a great variety of curves. Mereka digunakan ketika membuat model 3D, vector gambar, animasi, atau misalnya dalam definisi TrueType font. Ada banyak berbagai Curves. Some are easy to use, some are flexible enough to describe a large variety of shapes, and some are simple enough to be implemented and accelerated by graphics hardware. Beberapa yang mudah digunakan, ada pula yang cukup fleksibel untuk menjelaskan besar berbagai bentuk, dan ada pula yang cukup sederhana dan dilaksanakan oleh akselerasi hardware grafis.
NURBS and Bézier curves are ones of the most commonly used curves and the focus of this article. NURBS dan Bézier Curves adalah orang yang paling sering digunakan dan Curves fokus artikel ini.
Theory Teori
Bézier curves Bézier Curves
Before explaining NURBS, we will stop by Bézier curve, because NURBS is a generalization of Bézier curve. Sebelum menjelaskan NURBS, kami akan berhenti Bézier melengkung, karena NURBS adalah generalisasi dari Bézier curve. The following figure shows a simple Bézier curve (C), its control points (1), (2), (3), (4), and its control polygon (P). Berikut ini menunjukkan angka yang sederhana Bézier curve (C), dengan kontrol poin (1), (2), (3), (4), dan kontrol poligon (P). The control points are also called control handles. Kontrol poin juga disebut kontrol menangani.
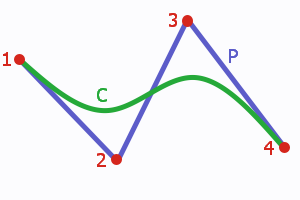
A cubic Bézier arc (C) with its control polygon (P). J kubik Bézier arc (C) dengan kontrol poligon (P).
Each point on a Bézier curve (and on many other kinds of curves) is computed as a weighted sum of all control points. This means that each point is influenced by every control point. Setiap titik di Bézier curve (dan pada banyak jenis Curves) adalah sebagai computed weighted jumlah semua titik kontrol. Ini berarti bahwa setiap titik dipengaruhi oleh setiap titik kontrol. The first control point has maximum impact on the beginning of the curve, the second one reaches its maximum in the first half of the curve, etc. Pertama yang memiliki kontrol maksimal pada awal melengkung, maka kedua mencapai maksimum pada setengah dari curve, dll
Each control point influences the final curve according to assigned blending function . A blending function defines the weight of the control point at each point of the curve. Kontrol terhadap setiap titik akhir melengkung sesuai dengan fungsi yang ditugaskan campuran. J campuran fungsi mendefinisikan berat kontrol titik di setiap sudut yang melengkung. A value of 0 indicates that the control point is not affecting a point on the curve. Nilai 0 menunjukkan bahwa kontrol adalah tidak mempengaruhi satu titik pada curve. If the blending function reaches 1, the curve is (usually) intersecting the control point. Jika fungsi campuran mencapai 1, curve adalah (biasanya) intersecting titik kontrol.
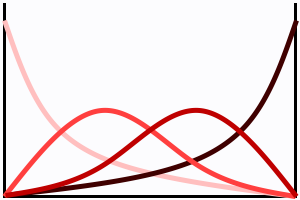
Blending functions of a cubic Bézier curve. Campuran dari fungsi kubik Bézier curve.
Four functions for four control points - each in different shade of red. Empat fungsi kontrol selama empat poin - masing-masing berbeda dalam bayangan merah.
Properties of blending functions define properties of a curve. Properti dari campuran menetapkan fungsi properti yang melengkung. Bézier curves use polynomial functions of given degree. The resulting curves have these properties: Bézier Curves jumlahnya banyak menggunakan fungsi diberi gelar. Hasilnya Curves ada properti ini:
- The curve starts in the first control point, ends in the last control point, but in general case does not cross the inner control points. Melengkung yang dimulai pada titik kontrol, berakhir pada titik kontrol, tetapi pada umumnya kasus tidak menyeberangi batin titik kontrol.
- The tangent of the curve in its ending points is controlled by the inner control points. Dengan persoalan yang melengkung dalam berakhir poin dikendalikan oleh batin titik kontrol.
- The curve is always inside the convex hull of the control polygon. Melengkung yang selalu di dalam lambung kapal cembung dari kontrol poligon.
Curve degree Curve gelar
The previous example showed a cubic (degree 3) curve, which is one of the most often used types. The degree refers to the highest exponent in the polynomial blending functions used for Bézier curves. A Bézier curve may be of arbitrary degree. Sebelumnya memperlihatkan contoh kubik (derajat 3) curve, yang merupakan salah satu jenis yang paling sering digunakan. Gelar yang merujuk kepada eksponen tertinggi dalam jumlahnya banyak fungsi yang digunakan untuk campuran Bézier Curves. Bézier J curve mungkin acak derajat. A degree 1 curve is a simple line and has two control points. A degree 2 curve is an arc and has three control points. J derajat 1 curve adalah garis sederhana dan memiliki dua titik kontrol. J 2 derajat curve adalah arc dan mempunyai tiga titik kontrol. The higher the degree, the more control points and the more complex shape is possible. Semakin tinggi gelar, semakin banyak titik kontrol yang lebih kompleks dan bentuk yang mungkin. But it is also more much harder to use, because each control point still influences the whole curve. Tetapi juga lebih banyak sulit untuk digunakan, karena setiap titik kontrol masih mempengaruhi seluruh curve.
Rational curves Rasional Curves
Each control point in rational curve is assigned a weight . Setiap titik kontrol rasional kurfa diberikan berat. The weight defines how much does a point "attract" the curve. Berat menentukan berapa banyak titik yang tidak "menarik" yang melengkung. Only the relative weights of the control points are important, not their absolute values. Hanya relatif bobot dari titik kontrol yang penting, mereka tidak mutlak nilai. A curve with all weights set to 1 will have the same shape as if all weights are set to 100. J melengkung dengan bobot semua set ke 1 akan memiliki bentuk yang sama seperti seolah-olah semua beban diatur ke 100. The shape only changes if weights of control points are different. Bentuk perubahan hanya jika kontrol bobot poin yang berbeda.
Ordinary Bézier curve is a special case or rational Bézier curve, where all weights are equal. Rational curve gives designers additional options at the cost of a more complicated algorithm and additional data to keep track of. Biasa Bézier curve adalah hal khusus atau rasional Bézier curve, di mana semua bobot yang sama. Rational kurfa desainer memberikan pilihan tambahan pada biaya yang lebih rumit dan algoritma data tambahan untuk menyimpan data.
B-Splines B-Splines
A B-Spline consists of multiple Bézier arcs and provides an unified mechanism how to define continuity in the joins. A B-Spline terdiri dari beberapa Bézier arcs dan menyediakan sebuah unified bagaimana mekanisme untuk menentukan kontinuitas di joins.
Consider two cubic Bézier curves - that is 8 total control points (4 per curve). Mempertimbangkan dua kubik Bézier Curves - yaitu kontrol 8 total poin (4 per curve).

B-Splines consist of Bézier arcs. B-Splines terdiri dari Bézier arcs.
Lets make the last point of the first (green) curve equal to the first point of the second (violet) curve - this saves us 1 point leaving us with 7 total control points. Lets membuat titik terakhir yang pertama (hijau) kurfa sama dengan titik pertama dari kedua (violet) curve - ini menyelamatkan 1 point kami meninggalkan kami dengan total 7 poin kontrol. We have replaced one control point with an external condition. Kami telah mengganti satu titik kontrol dengan kondisi eksternal.
The third (blue) curve and the fourth (yellow) curve share ending points just like in previous case, but and also share the same tangent direction at the junction point. Yang ketiga (biru) melengkung dan keempat (kuning) kurfa berbagi poin berakhir seperti dalam kasus sebelumnya, tetapi juga berbagi dan persoalan yang sama arah di titik persimpangan. There are two external conditions and only 6 control points are necessary to describe the curves. Ada dua kondisi eksternal dan hanya 6 titik kontrol yang diperlukan untuk menjelaskan Curves.
B-Splines use external conditions to put multiple pieces together while keeping the original concept of control points. B-Splines menggunakan kondisi eksternal untuk menempatkan beberapa lembar bersama sekaligus mempertahankan konsep asli titik kontrol. The neighbor curves share some control points. Curves berbagi dengan tetangga beberapa titik kontrol. External conditions are either implicit (uniform curves) or explicitly given by a knot vector . Eksternal kondisi baik implisit (seragam Curves) atau secara eksplisit diberikan oleh menyimpul vector. Knot vector defines how much information should be shared by neighbor curves (segments). Knot vector mendefinisikan berapa banyak informasi yang harus dibagi tetangga Curves (segmen).
Knot vector is a sequence of numbers, usually from 0 to 1, for example (0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.7, 1), and it holds the information about external conditions mentioned earlier. Knot vector merupakan urutan angka, biasanya 0-1, misalnya (0, 0.5, 0.5, 0,7, 1), dan memegang informasi tentang kondisi eksternal yang disebutkan sebelumnya. Number of intervals defines number of segments (3 in our case: 0-0.5, 0.5-0.7, 0.7-1). Numbers in knot vector are called knots and each knot has its multiplicity. Jumlah interval menentukan jumlah segmen (3 dalam kasus kami: 0-0,5, 0,5-0,7, 0.7-1). Angka dalam simpul disebut vector knot dan setiap simpul memiliki jumlah besar. Multiplicity of knot 0.7 is 1, while multiplicity of knot 0.5 is 2. Keserbaragaman dari simpul 0,7 adalah 1, sedangkan jumlah besar dari simpul 2 adalah 0,5. The higher the multiplicity, the less information share the neighbor segments. Semakin tinggi jumlah besar, semakin sedikit berbagi informasi segmen tetangga. When multiplicity is equal to the degree of used curves, there is a sharp edge (green and violet curves on the image). Ketika jumlah besar adalah sama dengan gelar yang digunakan Curves, terdapat ujung tajam (hijau dan violet Curves pada gambar).
NURBS NURBS
NURBS stands for Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline. NURBS adalah Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline. It means NURBS uses rational Bézier curves and an non-uniform explicitly given knot vector. Ini berarti menggunakan NURBS Curves Bézier rasional dan non-seragam yang diberikan secara eksplisit simpul vector. Therefore, degree, control points, weights, and knot vector is needed to specify a NURBS curve. Oleh karena itu, derajat, titik kontrol, bobot, dan simpul vector diperlukan untuk menentukan NURBS curve.
Curves, surfaces, volumes... Curves, permukaan, volume ...
So far, we were talking about curves - one-dimensional formations. Sejauh ini, kami berbicara tentang Curves - satu-dimensi yang membahana. The principles can be applied to higher-dimensional objects like surfaces or volumes. Surfaces are used when creating 3D objects, for example landscape while volumes can be used to define a non-linear transformation. Prinsip-prinsip yang dapat diterapkan ke dimensi yang lebih tinggi seperti permukaan benda atau volume. Permukaan digunakan saat membuat objek 3D, misalnya lansekap sementara volume dapat digunakan untuk menentukan transformasi non-linear.
Examples of NURBS curves Contoh NURBS Curves
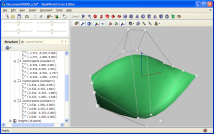
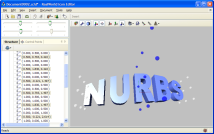
Following screenshots demonstrate different uses of NURBS in 3D graphics. Berikut screenshot menunjukkan berbeda yang menggunakan grafis 3D dalam NURBS.
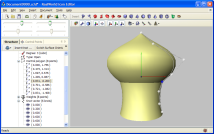
The left image demonstrates a surface created by revolving a 2D NURBS curve around Y axis. Sebelah kiri menunjukkan gambar yang dibuat oleh permukaan bergulir yang 2D NURBS curve sekitar Y axis. The curve itself consists of 3 pieces (knot vector: 0, 0.2, 0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1). Join between the two upper pieces is smooth, because the multiplicity of knot 0.2 is 1 and curve degree is 3. Curve itu sendiri yang terdiri dari 3 buah (simpul vector: 0, 0,2, 0,6, 0,6, 0,6, 1). Gabung antara dua buah atas adalah lancar, karena jumlah besar dari simpul 1 adalah 0,2 dan derajat curve adalah 3. On the other hand, knot 0.6 with multiplicity 3 causes a sharp edge. Di sisi lain, dengan simpul 0,6 keserbaragaman 3 penyebab yang tajam tajam.
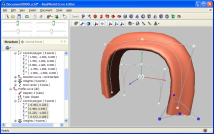
The right image shows a surface created by sweeping a 2D curve along a 3D trajectory. Sebelah kanan menampilkan gambar permukaan yang dibuat oleh sweeping 2D a 3D curve sepanjang lintasan.
Left image shows a NURBS surface and its control points. Kiri gambar menunjukkan NURBS permukaan dan titik kontrol. NURBS surfaces are used rather rarely in their pure form because the number of control points is usually large (4x4 in our simple case) and the surface becomes hard to control. NURBS permukaan agak jarang digunakan dalam bentuk murni karena jumlah titik kontrol biasanya besar (4x4 dalam kasus sederhana) dan permukaan menjadi sulit untuk mengendalikan.
Right image shows a 3D text that was transformed using a Bézier (or NURBS) volume of degree 2. Kanan menampilkan gambar 3D teks yang diwujudkan dengan menggunakan Bézier (atau NURBS) volume 2 derajat. The text is bent and its central part is larger - that effect was caused by the non-linear transformation defined by the NURBS volume (note the control points in the center of the model). Teks adalah bakat dan pusat adalah bagian yang lebih besar - yang merupakan efek yang disebabkan oleh non-linear transformasi ditentukan oleh NURBS volume (perhatikan titik kontrol di bagian tengah model).
Operations with NURBS Operasi dengan NURBS
When working with NURBS in their pure form, there is one very useful operation: inserting new knot . Ketika bekerja dengan NURBS dalam bentuk murni, ada satu operasi sangat berguna: memasukkan simpul baru. A knot can be inserted into a NURBS curve without changing the shape of the curve. J simpul dapat dimasukkan ke dalam NURBS melengkung tanpa mengubah bentuk melengkung. The desired side effect of this operation is an additional control point that provides finer control of the related region of the NURBS curve or surface. Efek samping yang dikehendaki dari operasi ini adalah titik kontrol tambahan yang menyediakan halus kontrol yang terkait dengan wilayah NURBS curve atau permukaan.
There are other operations with NURBS, like elevating degree, removing knots, or computing control point positions from points laying on a curve, but they do not reach the usefulness of knot insertion. Ada lainnya dengan NURBS, seperti elevating derajat, menghapus knot, atau komputasi titik kontrol poin dari posisi peletakan yang melengkung, tetapi mereka tidak mencapai manfaat simpul insersi.
Conclusion Kesimpulan
This article described the fundamentals of NURBS from users point of view by demonstrating their properties on simple examples. Artikel ini menggambarkan dasar dari pengguna NURBS dari sudut pandang mereka mendemonstrasikan oleh properti pada contoh sederhana.
While NURBS curves are relatively simple and anyone can learn to effectiveley use them after a bit of practice, NURBS surfaces are much harder due to the large amount of control points. Sementara NURBS Curves relatif sederhana dan setiap orang dapat belajar untuk menggunakannya effectiveley setelah sedikit prakteknya, NURBS permukaan juga lebih sulit karena besarnya jumlah titik kontrol. Therefore many applications offer various methods that simplify and limit their capabilities. Karena itu banyak aplikasi yang menawarkan berbagai metode yang mempermudah dan membatasi kemampuan mereka.
The problematic of curves in computer graphics is much larger than this introductory article indicates; readers are advised to seek other sources of information and to gain first hand experience. Yang bermasalah dari Curves grafis di komputer jauh lebih besar dari pengantar artikel ini menunjukkan; pembaca disarankan untuk mencari sumber informasi dan untuk mendapatkan pengalaman tangan pertama.

.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)




.jpg)




.jpg)



0 komentar:
Posting Komentar